Synthesis of a green magnetic biopolymer derived from oak fruit hull tannin for the efficient and simultaneous adsorption of a mixture of Malachite Green and Sunset Yellow dyes from aqueous solutions†
Abstract
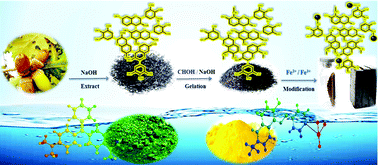
In the present study, a tannin-based magnetic porous organic polymer using the internal layer of oak fruit hull (oak Gal) extract was synthesized as a new bioadsorbent with polyhydroxyphenyl groups. The resulting product, magnetic oak tannin gel (Fe3O4–OT), was tested for the efficient and simultaneous adsorption of cationic (Malachite Green, MG) and anionic (Sunset Yellow, SY) dyes from their mixture in aqueous solutions. For MG and SY, concentration determination and the problems caused by the overlap of the spectrum of the dye, first-order derivative spectrophotometry was used to analyze the simultaneous absorption of the two dyes. The structural, morphological and magnetic property functionalization of Fe3O4–OT was confirmed by FE-SEM, XRD, FTIR spectroscopy, VSM, BET/BJH, and by studying isotherms, kinetics, diffusion, and thermodynamics parameters of adsorption. The response surface methodology (RSM) using a central composite (CCD) combined design was then used to design the experiments and optimize the process. Accordingly, the adsorption capacities of MG and SY dyes measured by the Langmuir adsorption model were 49.00 and 53.95 mg g−1, respectively, at optimum conditions such as Fe3O4–OT dose of 0.02 g L−1, pH of 6.5, and dye concentration of 16 mg L−1 for 20 min. Adsorption on Fe3O4–OT followed the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. In addition, the thermodynamic parameters specified that the adsorption process was spontaneous and endothermic. All the experimental results showed that the Fe3O4–OT bioadsorbent would be an ideal and green adsorbent with reusability combined to remove cationic and anionic dyes from wastewater and can be rapidly and easily extracted from wastewater using an external magnetic field.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...