1st generation dendrimeric antioxidants containing Meldrum's acid moieties as surface groups†
Abstract
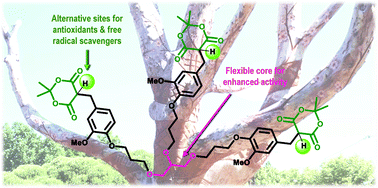
Free radical-caused oxidative stress can be reduced by various antioxidants. A new and promising type of antioxidant are monosubstituted Meldrum's acids. Herein the first dendritic architecture with 1,3-dioxane-4,6-dione units as surface groups is presented. The compounds were synthesized through the alkylation of phenol, the Knoevenagel condensation and sequential reduction. The antiradical activity (AA) against 1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl hydrazyl (DPPH) for all compounds is 80–90%, and the IC50 varies from 10–35 μM. These data are comparable with vitamin C, t-butylhydroquinone (TBHQ) or vitamin E. The AA against galvinoxyl (GO) increased with the number of surface groups. The AA was comparable with butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) for compounds with at least two moieties of 1,3-dioxane-4,6-dione. The structure with a flexible glycerol core is highlighted among all the derivatives. Although the AA against DPPH for the glycerol derivative is comparable with those with aromatic cores it is more effective against GO (AA = 95%, IC50 = 60 μM): the AA is greater than for vitamin C and BHT. Thus, a flexible structure seems to be a promising core for elaborating powerful antioxidants with Meldrum's acid surface groups.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...