Construction of biocatalytic cascades for the synthesis of benzylisoquinoline alkaloids from p-coumaric acid derivatives and dopamine†
Abstract
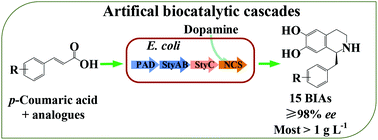
Benzylisoquinoline alkaloids (BIAs) are an important family of plant-derived metabolites with diverse biological activities. Owing to their structural complexity and high stereoselectivity, the efficient synthesis of BIAs is challenging. The construction of heterologous pathways based on synthetic biology has shown potential for the efficient production of BIAs. This study demonstrates a bioconversion strategy by constructing the biocatalytic decarboxylation–epoxidation–isomerization–condensation cascades for the synthesis of BIAs from p-coumaric acid derivatives and dopamine. Firstly, the feasibility of this strategy was verified by investigating the synthesis of (S)-norcoclaurine from p-coumaric acid and dopamine. Then the synthesis of BIAs was expanded using different p-coumaric acid derivatives as substrates, and a total of 15 BIAs were synthesized with excellent enantioselectivity (≥98% ee), with more than half having concentrations greater than 1 g L−1. Furthermore, to demonstrate the applications of renewable raw materials, the synthesis of (S)-norcoclaurine using lignocellulosic biomass hydrolysate rich in p-coumaric acid as the key substrate was investigated, in which 1.2 g L−1 of (S)-norcoclaurine was achieved with 90% conversion and >98% ee. This study shows not only a promising strategy to enable sustainable synthesis of diverse BIAs, but also an alternative way to improve the utilization of lignocellulosic biomass to synthesize value-added natural products.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...