The combination of sodium alginate and chlorogenic acid enhances the therapeutic effect on ulcerative colitis by the regulation of inflammation and the intestinal flora
Abstract
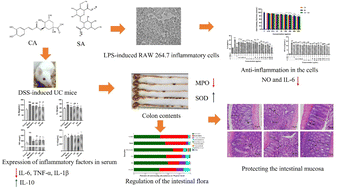
Chlorogenic acid (CA) and sodium alginate (SA) each have good therapeutic effects on ulcerative colitis (UC) owing to their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity. This study aimed to investigate the effects of CA alone and in combination with SA on inflammatory cells and UC mice. In the Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced RAW 264.7 inflammatory cell model, Nitric oxide (NO) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels were significantly lower after treatment with CA plus SA than with CA alone. In the DSS-induced UC mouse model, compared with CA alone, CA plus SA showed a better ability to alleviate weight loss, reduce the disease activity index (DAI), improve the colonic mucosa, reduce the expression of inflammatory factors in the serum and myeloperoxidase (MPO) in colonic tissue, increase superoxide dismutase (SOD) levels, protect the intestinal mucosa and regulate the abundance of Actinobacteriota, Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Bacteroides, Subdoligranulum and Streptococcus. Thus, CA plus SA can improve the therapeutic efficacy of CA in UC by regulating inflammatory factors, oxidative stress, and the intestinal flora and by protecting ulcerative wounds. These findings broaden our understanding of the role of the combination of SA and CA in enhancing the effects of CA on UC and provide strategies for prevention and treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...