Inhibitory effects of Centella asiatica (L.) Urban on enlarged prostate through androgen receptor and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways
Abstract
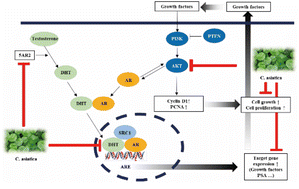
Centella asiatica (L.) Urban (C. asiatica) is a traditional herbal medicine that has been used for wound healing and anti-inflammation since ancient times. Various biological effects of C. asiatica ethanolic extract (CAE) were previously reported. However, in our previous study, C. asiatica aqueous extract (CAA) exhibited higher inhibitory activity on benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) than CAE. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate the effect of CAA on BPH, and elucidate the inhibitory mechanism through in vitro and in vivo experiments as well as metabolite analysis of CAA. A BPH rat model was induced by daily subcutaneous injection of testosterone propionate (TP, 3 mg kg−1) dissolved in corn oil for 4 weeks after castration. The experimental group, the CAA treatment group, was orally administered CAA (100 mg kg−1) for 4 weeks while inducing prostatic hyperplasia. Saw palmetto extract (Saw, 100 mg kg−1) and Finasteride (Fi, 1 mg kg−1) were used as positive controls and were administered orally for 4 weeks. CAA significantly inhibited androgen receptor signaling related factors overexpressed by dihydrotestosterone (DHT) treatment in prostate cell lines. Afterwards, the testosterone-induced BPH model was used to verify the alleviation efficacy of CAA in prostatic hyperplasia. Prostate size and the thickness of the prostate tissue epithelium were significantly decreased in the group treated with CAA compared to those in the BPH group. The results of protein expression in the prostate tissue confirmed that CAA inhibited androgen receptor signaling in BPH and decreased the expression of growth factors. Moreover, CAA suppressed the expression of the PI3K/Akt pathway and cell proliferation-related factors compared to the BPH group. Taken together, these results indicate that CAA improves the inhibitory efficacy of BPH by inhibiting the androgen receptor and PI3K/Akt pathways, suggesting that CAA may be a promising candidate for biopharmaceutical formulations of BPH.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...