Lactation-dependent vertical transmission of natural probiotics from the mother to the infant gut through breast milk†
Abstract
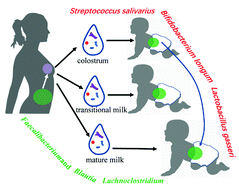
The transmission of certain bacteria from the mother's gut to the infant's gut via breast milk (BM) is critical for the offspring's immune system development. Dysbiosis of the BM microbiota can be caused by a variety of reasons, which can be influenced by probiotics delivered via the enteromammary route. The goal of this study was to investigate the bacteria that can be transmitted from the mother to the infant's intestine during various lactation periods in 19 mother–child dyads. Bacterial transmission is most common during the colostrum phase when bacteria with certain amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) enter the newborn intestine and inhabit it permanently. We have established that anaerobic gut-associated bacteria, such as Faecalibacterium, Blautia and Lachnoclostridium, transfer from the mother to the infant's gut with lactation dependence using the idea of weighted transfer ratios. Streptococcus salivarius, Bifidobacterium longum, and Lactobacillus gasseri are transferred from the maternal gut to the BM, as well as from the BM to the newborn gut, depending on different ASVs. These findings suggest that isolation of key microorganisms from breast milk could be utilized to modify the microbiota of BM or newborns by giving the mother a probiotic or adding it to artificial milk to promote neonatal health.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...