Dietary gamma-aminobutyric acid ameliorates growth impairment and intestinal dysfunction in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) fed a high soybean meal diet†
Abstract
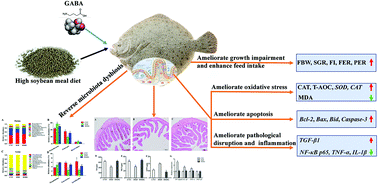
Over-substitution of fishmeal with soybean meal (SBM) commonly induces inferior growth and intestinal dysfunction in fish. This study aims to evaluate whether dietary gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) could ameliorate the adverse effects in turbot fed a high-SBM diet (HSD). Two hundred and seventy turbots were randomly divided into three treatment groups including turbots fed on a control diet (CNT, containing 60% fishmeal), an HSD (with 45% fishmeal protein replaced by SBM), and an HSD supplemented with GABA (160 mg kg−1) for 53 days. The growth and feed utilization parameters were calculated and the intestinal antioxidant status, inflammation, apoptosis, and microbiota were evaluated using assay kits, histological analysis, qRT-PCR, high throughput sequencing, and bioinformatics analysis. The results showed that GABA ameliorated HSD-induced growth impairment and enhanced feed intake of turbot. GABA ameliorated HSD-induced intestinal oxidative stress and apoptosis by restoring the MDA content, CAT and T-AOC activities, and apoptosis-related gene (Bcl-2, Bax, Bid, and Caspase-3) expressions to similar levels to those in the CNT group. GABA also alleviated HSD-induced intestinal inflammation through down-regulating the expressions of TNF-α, IL-1β, and NF-κB p65 and up-regulating the expression of TGF-β1. Furthermore, GABA reversed HSD-induced microbiota dysbiosis through regulating the overall bacterial richness and dominative bacterial population. Spearman's correlation analysis indicated that the altered microbiota was closely associated with growth and intestinal function. Collectively, GABA could ameliorate HSD-induced intestinal dysfunction via relieving oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis and microbiota dysbiosis, and these findings would contribute to a better understanding of the function of GABA in the fish intestine.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...