Exploring the Zn-regulated function in Co–Zn catalysts for efficient hydrogenation of ethyl levulinate to γ-valerolactone†
Abstract
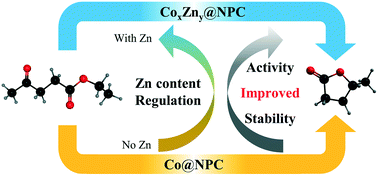
A series of CoZn catalysts supported on N-doped porous carbon (CoxZny@NPC-T) with controlled Zn content prepared at different calcination temperatures are studied for catalytic hydrogenation of biomass-based ethyl levulinate to γ-valerolactone, in which Zn is introduced as a regulator. The catalytic activity of optimum Co3Zn1@NPC-600 is 13 times higher than that of Co@NPC-600. The high activity of the catalyst is attributed to the Zn content: the amount of Zn not only regulates the content of active Co(0) and promotes the activation of hydrogen, but also affects the content of acidic sites and optimizes the adsorption of intermediates. Meanwhile, the content of Zn will also optimize the structural characteristics of the catalyst, thereby increasing the dispersion of active sites and mass transfer of the substrate. The regulated function of the Zn content, including electronic effects, acid site effects and size effects, is discussed in detail. In addition, the doping of Zn also helps to improve the stability of cycling performance. The strategy of adjusting the catalytic performance by the doping content provides support and examples for the rational design of highly active and stable catalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...