A simple epoxy resin screen-printed paper-based analytical device for detection of phosphate in soil
Abstract
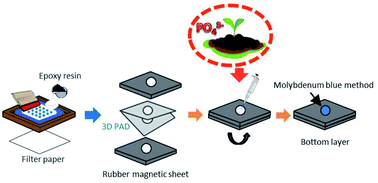
This study develops a simple and low-cost 3D paper-based analytical device (3D PAD) for the detection of available phosphate in soil. Epoxy resin is presented as a new hydrophobic material for low-cost mass production of PADs using the screen-printing method. An optimized concentration of epoxy resin solution is screen printed onto Whatman filter paper no. 1 in an easy one-step process to create hydrophobic patterns on PADs. The epoxy resin is air dried at room temperature, without heating or UV curing. This method delivers high reproducibility, resolution, and stability, and the epoxy resin barrier is compatible with both organic solvents and aqueous solutions. The molybdenum blue method is used in this PAD to measure phosphate in a colorimetric assay. The developed 3D PAD attains a linear range of 0.5–40 mg L−1, with a limit of detection (LOD) of 0.25 mg L−1, and a limit of quantitation (LOQ) of 0.83 mg L−1. The relative standard deviation of intra-day measurements is 1.52–2.46%, and the inter-day standard deviation is 1.89–2.74%, indicating satisfactory reproducibility. This 3D PAD was tested for its ability to detect phosphate in a variety of actual soil samples and the results were validated against spectrophotometric analysis using a paired t-test, which showed high accuracy. In short, the new analytical device described in this study is simple, fast, and inexpensive to make and use, providing a versatile phosphate detection tool for many soil types, even in situations when resources are limited.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...