Microfluidics-based rapid measurement of nitrite in human blood plasma†
Abstract
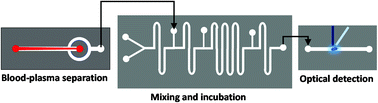
Nitric oxide (NO) is one of the vital gasotransmitters that takes part in many biological pathways such as infection, inflammation and ischemia, immune response, neurotransmission, and cardiovascular systems. Nitrite is one of the primary metabolites of NO and is considered to be a circulating storage pool for NO. Here, we report direct and rapid measurement of nitrite in human blood plasma using a fluorescence-based microfluidic method. The study revealed the factors that affect the endogenous concentration of nitrite in blood plasma, mainly the presence of blood cells, hemoglobin, and soluble proteins. We find that separation of blood plasma immediately after sample collection and subsequent dilution of plasma with buffer at a ratio of 1 : 4 eliminates the interference from cells and proteins, providing reliable measurements. The proposed method can measure plasma nitrite in the concentration range of 0–20 µM with a limit of detection of 60 nM and a sensitivity of 5.64 µM−1 within 10 min of sample collection. By spiking nitrite into plasma, a linear correlation between the nitrite concentration and FL intensity is obtained, which is utilized further to measure the endogenous concentration of nitrite present in the plasma of healthy volunteers and patients. The study revealed that the endogenous nitrite concentration in the blood plasma of healthy humans falls in the range of 0.4–1.2 µM. Furthermore, the study with blood samples obtained from patients showed that nitrite levels are inversely correlated with the total cholesterol and low-density lipoproteins levels, which is in good agreement with the literature.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...