Formation of asymmetric belt-like aggregates from a bio-based surfactant derived from dehydroabietic acid†
Abstract
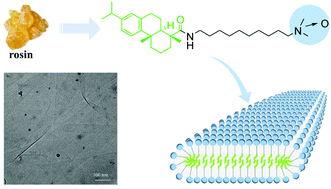
The morphology and physicochemical properties of ordered molecular aggregates are closely related to surfactant molecules. Herein, a rosin-based amine oxide surfactant containing a large hydrophobic group (abbreviated R-10-AO) was synthesized from dehydroabietic acid, which is an important derivative of rosin. Cryogenic transmission electron microscopy (cryo-TEM) images and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) showed that at a concentration of ∼5 mM, R-10-AO molecules formed flexible nanobelts with a thickness of only 2–3 nm. The width of these nanobelts was 50–150 nm and the length was more than 1 μm. The formation of the stable nanobelts arose from the strong van der Waals forces of the bulky hydrophobic portions of R-10-AO in solution, facilitating the stability of the asymmetrical aggregates. Rheological tests showed that the formed nanobelts were thermodynamically stable. The entanglement of these nanobelts led to significant viscoelasticity of the solutions. The zero-shear viscosity (η0) of the R-10-AO solution reached 10 Pa s at a concentration of 5 mM, which is much greater than that of most wormlike micellar solutions. This work provides the inspirations of preparing aggregates with novel properties using natural products.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...