Elucidating the structure-dependent selectivity of CuZn towards methane and ethanol in CO2 electroreduction using tailored Cu/ZnO precatalysts†
Abstract
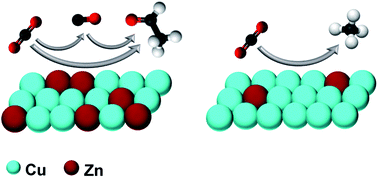
Understanding the catalyst compositional and structural features that control selectivity is of uttermost importance to target desired products in chemical reactions. In this joint experimental–computational work, we leverage tailored Cu/ZnO precatalysts as a material platform to identify the intrinsic features of methane-producing and ethanol-producing CuZn catalysts in the electrochemical CO2 reduction reaction (CO2RR). Specifically, we find that Cu@ZnO nanocrystals, where a central Cu domain is decorated with ZnO domains, and ZnO@Cu nanocrystals, where a central ZnO domain is decorated with Cu domains, evolve into Cu@CuZn core@shell catalysts that are selective for methane (∼52%) and ethanol (∼39%), respectively. Operando X-ray absorption spectroscopy and various microscopy methods evidence that a higher degree of surface alloying along with a higher concentration of metallic Zn improve the ethanol selectivity. Density functional theory explains that the combination of electronic and tandem effects accounts for such selectivity. These findings mark a step ahead towards understanding structure–property relationships in bimetallic catalysts for the CO2RR and their rational tuning to increase selectivity towards target products, especially alcohols.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...