MoS2-assisted Fe2+/peroxymonosulfate oxidation for the abatement of phenacetin: efficiency, mechanisms and toxicity evaluation†
Abstract
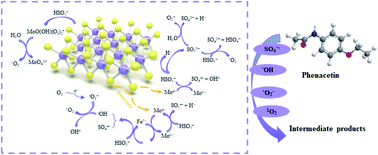
In this study, molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) was chosen as a co-catalyst to enhance the removal efficiency of phenacetin (PNT) in water by a ferrous ion-activated peroxymonosulfate (Fe2+/PMS) process. Operating parameters, such as the initial solution pH and chemical dose on PNT degradation efficiency were investigated and optimized. Under an initial pH of 3, an Fe2+ dose of 25 μM, a PMS dose of 125 μM and a MoS2 dose of 0.1 g L−1, the degradation efficiency of PNT reached 94.3%, within 15 min. The presence of common water constituents including Cl−, HCO3−, SO42− and natural organic matter (NOM) will inhibit degradation of PNT in the MoS2/Fe2+/PMS system. Radical quenching tests combined with electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) results indicated that in addition to free radical species (˙OH, SO4˙− and O2˙−), nonradical reactive species (1O2) were also crucial for PNT degradation. The variations in the composition and crystalline structure of the MoS2 before and after the reaction were characterized by XPS and XRD. Further, the degradation pathways of PNT were proposed according to the combined results of LC/TOF/MS and DFT calculations, and primarily included hydroxylation of the aromatic ring, cleavage of the C–N bond of the acetyl-amino group, and cleavage of the C–O bond of the ethoxy group. Finally, toxicity assessment of PNT and its products was predicted using the ECOSAR program.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...