Novel pyrimidine-bichalcophene derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for copper in 1 M nitric acid solution
Abstract
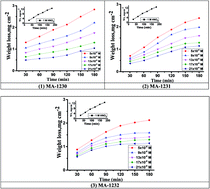
This study targets the investigation of three pyrimidine-bichalcophene derivatives (MA-1230, MA-1231, MA-1232) for the prevention of corrosion on copper in 1 M HNO3 via weight loss (WL), potentiodynamic polarization (PDP), and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) techniques. The surface morphology was also analyzed by different methods. It was found that the inhibition efficiency (% η) increased by increasing the doses of pyrimidine derivatives and the temperature of the medium. Weight loss data revealed the better adsorption of MA-1232 on the Cu surface at increased inhibitor dose, reaching a maximum efficiency of 99.14% at a dose of 21 μM at 45 °C. The best description of the adsorption of the investigated derivatives on the copper surface was given by the Langmuir isotherm. Some important thermodynamic parameters for the studied inhibitors were computed and are discussed herein. The polarization studies showed that the pyrimidine-bichalcophenes act as mixed inhibitors. Computational chemical approaches were used with informative yields, including quantum-chemical and molecular dynamics simulation techniques, which agree with the experimental results. The results obtained from all tested methods are strongly accepted.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...