Unique hierarchical SiO2@ZnIn2S4 marigold flower like nanoheterostructure for solar hydrogen production†
Abstract
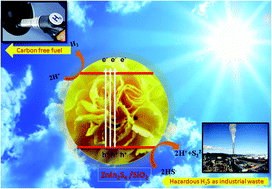
The novel marigold flower like SiO2@ZnIn2S4 nano-heterostructure was fabricated using an in situ hydrothermal method. The nanoheterostructure exhibits hexagonal structure with marigold flower like morphology. The porous marigold flower assembly was constructed using ultrathin nanosheets. Interestingly, the thickness of the nanopetal was observed to be 5–10 nm and tiny SiO2 nanoparticles (5–7 nm) are decorated on the surface of the nanopetals. As the concentration of SiO2 increases the deposition of SiO2 nanoparticles on ZnIn2S4 nanopetals increases in the form of clusters. The optical study revealed that the band gap lies in the visible range of the solar spectrum. Using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), the chemical structure and valence states of the as-synthesized SiO2@ZnIn2S4 nano-heterostructure were confirmed. The photocatalytic activities of the hierarchical SiO2@ZnIn2S4 nano-heterostructure for hydrogen evolution from H2S under natural sunlight have been investigated with regard to the band structure in the visible region. The 0.75% SiO2@ZnIn2S4 showed a higher photocatalytic activity (6730 μmol−1 h−1 g−1) for hydrogen production which is almost double that of pristine ZnIn2S4. Similarly, the hydrogen production from water splitting was observed to be 730 μmol−1 h−1 g−1. The enhanced photocatalytic activity is attributed to the inhibition of charge carrier separation owing to the hierarchical morphology, heterojunction and crystallinity of the SiO2@ZnIn2S4.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...