Effect of axial molecules and linker length on CO2 adsorption and selectivity of CAU-8: a combined DFT and GCMC simulation study†
Abstract
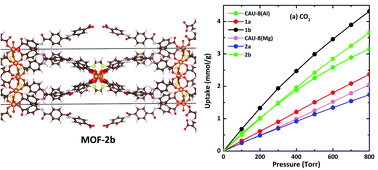
Density Functional Theory (DFT) and Grand Canonical Monte Carlo (GCMC) calculations are performed to study the structures and carbon dioxide (CO2) adsorption properties of the newly designed metal–organic framework based on the CAU-8 (CAU stands for Christian-Albrechts Universität) prototype. In the new MOFs, the 4,4′-benzophenonedicarboxylic acid (H2BPDC) linker of CAU-8 is substituted by 4,4′-oxalylbis(azanediyl)dibenzoic acid (H2ODA) and 4,4′-teraphthaloylbis(azanediyl)dibenzoic acid (H2TDA) containing amide groups (–CO–NH- motif). Furthermore, MgO6 octahedral chains where dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) decorating the axial position bridged two Mg2+ ions are considered. The formation energies indicate that modified CAU-8 is thermodynamically stable. The reaction mechanisms between the metal clusters and the linkers to form the materials are also proposed. GCMC calculations show that CO2 adsorptions and selectivities of Al-based MOFs are better than those of Mg-based MOFs, which is due to DMSO. Amide groups made CO2 molecules more intensively distributed besides organic linkers. CO2 uptakes and selectivities of MOFs containing H2TDA linkers are better in comparison with those of MOFs containing H2BPDC linkers or H2ODA linkers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...