A monodispersed CuPt alloy: synthesis and its superior catalytic performance in the hydrogen evolution reaction over a full pH range†
Abstract
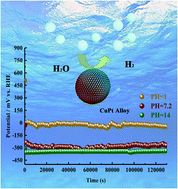
The high cost and low stability of electrocatalysts are the major challenges for the commercialization of hydrogen generation in water. In this study, we demonstrated a one-pot synthesis of a monodispersed CuPt alloy with the diameter range of 20–30 nm by a hydrothermal method. Benefiting from the more available active sites and preferable d-band structure, the CuPt alloy exhibited a superior catalytic performance than pure Pt nanoparticles (Pt NPs) in the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). In acidic media, the CuPt alloy achieved a low overpotential of 39 mV at a current density of 10 mA cm−2 for HER, which was by 22 mV lower than that for pure Pt NPs. In a neutral solution, the stability of the CuPt alloy is ca. 100-fold as compared to pure Pt NPs. Accounting by the dissolution of Cu in the alloy phase, the performance of the CuPt alloy was elevated after yielding hydrogen for 1.2 × 105 s in alkaline media. The superior catalytic activity can also be applied in other applications. In the reduction of 4-nitro-phenol (4-NP), the CuPt alloy showed 12.84-fold catalytic activity higher than pure Pt NPs. This study designed a low-cost electrocatalyst with an efficient and durable catalytic performance for HER over the full pH range, which provides an environmentally friendly strategy to cope with the challenges of hydrogen generation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...