Quantitative evaluation of the non-thermal effect in microwave induced polymer curing†
Abstract
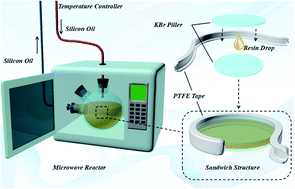
Microwave irradiation is one of the most effective strategies to accelerate the curing of resin. However, the mechanism is still unclear. The debates mainly focus on how to quantitatively evaluate the ‘non-thermal’ effect of the microwave. In this work, the non-thermal effect on DGEBA with amine (D230) and anhydride (MHHPA) hardeners respectively was evaluated via an isothermal microwave curing reactor. The ‘thermal effect’ caused by the microwave was peeled off accurately. Iso-conversional kinetic analysis was performed based on the reaction extent from the real time FTIR spectrum, and the apparent activation energy (Ea) was calculated for the quantitative evaluation of the microwave non-thermal effect. The influence caused by the polarized functional groups, reaction temperature and the transition state were explored, and the microwave non-thermal effect on the mechanical performance of the cured thermosets was evaluated. Results indicated that the microwave non-thermal effect was able to reduce the Ea and accelerate the curing speed of epoxy resin. At the same time, the final curing extent was increased when the non-thermal effect of microwave was induced leading to enhanced mechanical and thermal performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...