The broad amine scope of pantothenate synthetase enables the synthesis of pharmaceutically relevant amides†
Abstract
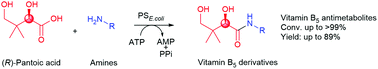
Pantothenate synthetase from Escherichia coli (PSE. coli) catalyzes the ATP-dependent condensation of (R)-pantoic acid and β-alanine to yield (R)-pantothenic acid (vitamin B5), the biosynthetic precursor to coenzyme A. Herein we show that besides the natural amine substrate β-alanine, the enzyme accepts a wide range of structurally diverse amines including 3-amino-2-fluoropropionic acid, 4-amino-2-hydroxybutyric acid, 4-amino-3-hydroxybutyric acid, and tryptamine for coupling to the native carboxylic acid substrate (R)-pantoic acid to give amide products with up to >99% conversion. The broad amine scope of PSE. coli enabled the efficient synthesis of pharmaceutically-relevant vitamin B5 antimetabolites with excellent isolated yield (up to 89%). This biocatalytic amide synthesis strategy may prove to be useful in the quest for new antimicrobials that target coenzyme A biosynthesis and utilisation.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Catalysis & biocatalysis in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...