Metabolomics in infectious diseases and drug discovery
Abstract
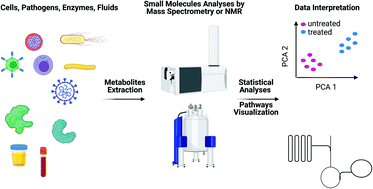
Metabolomics has emerged as an invaluable tool that can be used along with genomics, transcriptomics and proteomics to understand host–pathogen interactions at small-molecule levels. Metabolomics has been used to study a variety of infectious diseases and applications. The most common application of metabolomics is for prognostic and diagnostic purposes, specifically the screening of disease-specific biomarkers by either NMR-based or mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. In addition, metabolomics is of great significance for the discovery of druggable metabolic enzymes and/or metabolic regulators through the use of state-of-the-art flux analysis, for example, via the elucidation of metabolic mechanisms. This review discusses the application of metabolomics technologies to biomarker screening, the discovery of drug targets in infectious diseases such as viral, bacterial and parasite infections and immunometabolomics, highlights the challenges associated with accessing metabolite compartmentalization and discusses the available tools for determining local metabolite concentrations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...