Differential N-glycosylation profiling of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) invasive ductal carcinoma tissues using MALDI-TOF-MS†
Abstract
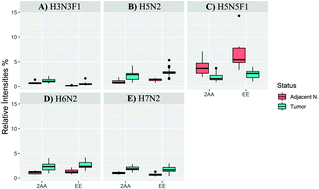
Invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) is the most common type of breast cancer. As dynamic changes of the glycome are closely associated with complex diseases, they have become a focal point of cancer research involving predictive and prognostic markers. Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) clinical specimens are representative of the tumor environment and are thus utilized in studies on cancer related research and biomarker discovery. Further studies on differential N-glycosylation profiling of IDC cancer tissues are necessary in order to understand the biological role of glycans in cancer and to evaluate their predictive ability. In this study, matrix assisted laser desorption ionization-mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS)-based analyses were conducted for determining differential N-glycosylation patterns of IDC. Two different derivatization methods, namely, 2-aminobenzoic acid (2-AA) labeling and linkage-specific sialic acid esterification, were used for the analysis of N-glycans. Forty-seven 2-AA labeled and fifty ethyl esterified N-glycans were identified by MALDI-MS. In statistical analyses conducted for 2-AA-labeled N-glycans, the relative amounts of 32 N-glycans and prevalence of 15 N-glycan traits showed significant (p < 0.05) differences between cancer and normal tissues; and in such analyses for the ethyl-esterified N-glycans, the relative amounts of 27 N-glycans and prevalence of 17 N-glycan traits showed significant (p < 0.05) differences between them. It was found that mainly high mannose N-glycans, including H5N2, H6N2, and H7N2, and two fucosylated compositions (H3N3F1 and H5N5F1) showed strong discrimination between IDC and controls. In addition, compared with the controls, high mannose N-glycans were observed to be up-regulated in IDC whereas bisecting N-glycans were down-regulated.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...