Anion effects on the properties of OIPC/PVDF composites†
Abstract
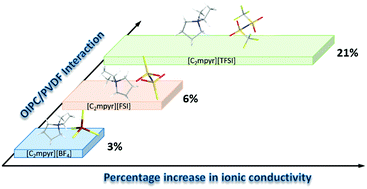
Organic ionic plastic crystals (OIPCs) are promising solid electrolytes because of their inherent advantages such as non-volatility, non-flammability, good thermal stability, favourable plasticity, and improved electrolyte/electrode interfacial contact. Incorporating nanoparticles into some OIPC matrixes has proven an effective strategy for further increasing conductivity and mechanical integrity. However, the nature of the interaction between the cations and anions of OIPCs with polymers requires further study. In this work, various OIPCs consisting of N-ethyl-N-methyl pyrrolidinium cations ([C2mpyr]+) and three different anions bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide ([TFSI]−), (bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide ([FSI]−) and tetrafluoroborate, [BF4]−) are selected. The interactions between the OIPCs and poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) are studied by incorporating different volume fractions of PVDF nanoparticles into the OIPC matrices. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and synchrotron X-ray diffraction (XRD) techniques confirm that the OIPCs with different anions interact differently with PVDF. Furthermore, we propose that the degree of the interaction and ionic conductivity enhancement relates to different dipole moments of the OIPC anions. This anion originated interaction induces the formation of disordered OIPC interphases which accounts for the ionic conductivity enhancement.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...