Stable cycling via absolute intercalation in graphite-based lithium-ion battery incorporated by solidified ether-based polymer electrolyte†
Abstract
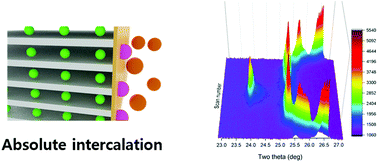
Current lithium-ion batteries are vulnerable to fire accidents and explosions because liquid electrolytes have a low flash point and poor thermal stability. This intrinsic problem has led to an ever-growing interest in solid-state polymer electrolytes with high thermal stability. In this study, a solidified polyether-based polymer electrolyte is incorporated into a graphite/LiFePO4 full-cell battery. A liquid precursor, which is prepared by mixing the bisphenol A ethoxylate diacrylate (BisA) crosslinker and the poly(ethylene glycol) dimethyl ether (PEGDME) plasticizer, first wets the anode and cathode, and is then solidified by in situ thermal crosslinking to produce a solid polymer electrolyte. BisA forms a rigid crosslinked network and PEGDME conducts lithium ions within the network. Analysis results, including in situ X-ray diffraction, show that PEGDME in the polymer electrolyte is co-intercalated with lithium ions into the gallery of the graphite electrode, which causes electrode exfoliation and severe capacity fading. Fluoroethylene carbonate is highly effective to prevent the co-intercalation of lithium–PEGDME complex ions into the graphite, via the formation of a solid electrolyte interphase layer, which leads to the ‘absolute intercalation’ of lithium ions. Consequently, the graphite/LiFePO4 full-cell battery based on the solid polymer electrolyte runs stably at a coulombic efficiency higher than 99% for most cycles and the residual capacity of the cell reaches 80% after 100 cycles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...