Nuciferine administration in C57BL/6J mice with gestational diabetes mellitus induced by a high-fat diet: the improvement of glycolipid disorders and intestinal dysbacteriosis†
Abstract
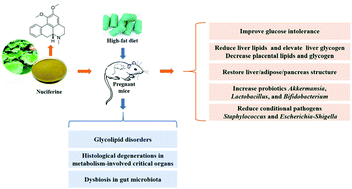
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) has become a global health concern as the main result of its contribution to the high risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes for both the mother and fetus. However, there is absence of an ideal and widely acceptable therapy. Nuciferine has previously been shown to exert beneficial effects in various metabolic diseases. This study aimed to investigate the potential therapeutic efficacy of nuciferine on GDM in C57BL/6J mice induced by a high-fat diet (HFD), which has not been reported before. The results showed that nuciferine improved glucose intolerance, reduced lipid accumulation and increased the glycogen content within hepatocytes, and decreased placental lipid and glycogen deposition, thus ameliorating glycolipid disorders in GDM mice. Additionally, nuciferine protected against histological degeneration of metabolism-associated critical organs including the liver, pancreas, and abdominal adipose tissue. Most interestingly, nuciferine could correct intestinal dysbacteriosis in GDM mice, as evidenced by the elevation of probiotic abundances consisting of Akkermansia, Lactobacillus, and Bifidobacterium, which were all negatively correlated with serum and liver triglyceride (TG) and positively associated with hepatic glycogen, and the reduction of conditional pathogen abundances including Escherichia–Shigella and Staphylococcus, and the latter was positively related to serum and liver TG and negatively linked with liver glycogen. Collectively, these findings suggest that nuciferine as a food-borne strategy played important roles in the management of GDM.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...