Prolonged continual consumption of oregano herb interferes with the action of steroid hormones and several drugs, and effects signaling across the brain–gut axis†
Abstract
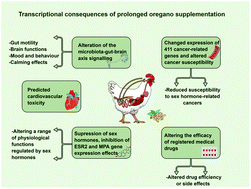
Herbs and spices have been used throughout human history for their medicinal qualities. The advent of cheap and readily available medicines have lessened the need for herbs and spices as traditional medicines, however, they are rapidly regaining popularity with rising interest of the general population in health, natural products and nutrition. The need for alternative medicines with antimicrobial properties, such as herbs and spices, has also come to the forefront in light of the recent bans of antibiotic use in the livestock industry, including the poultry industry. This large scale use presents an opportunity to observe nutrigenomic effects of prolonged use of herbs on a substantial number of birds fed high concentrations of these products throughout the production cycle. In this manuscript, we investigated the transcriptional effect of continual prolonged oregano supplementation on chicken ileum gene expression. Based on ileum transcriptomics, we report that continual supplementation with 2% oregano altered microbiota-gut–brain axis signalling, rearranged cancer susceptibility towards reduced steroid hormone-related cancers and altered expression of genes targeted by many registered drugs, thus likely affecting their efficiency and side effects. Transcriptional toxicology analysis indicated significant activation of Ventricular Septal Defect and Congenital Heart Disease categories. Our results, counter the notion that natural products such as oregano have the potential for little to no side-effects as they are “natural”. The nutrigenomic approach of understanding benefits and side effects of the food we eat, can revolutionize disease management and therapy and have special significance in designing the diets for individuals or livestock with known disease predispositions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...