Effect of extrusion processing and addition of purple sweet potatoes on the structural properties and in vitro digestibility of extruded rice
Abstract
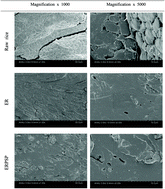
Recently, extruded rice as a functional ingredient has been a hot area of research in food processing. In this study, extruded rice with purple sweet potato (ERPSP) was prepared. Moreover, the effects of extrusion and added purple sweet potato on the structure and in vitro digestibility of extruded rice were studied via numerous detection methods, such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM), water absorption index (WAI), water solubility index (WSI), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). SEM results showed that there were numerous pits and bubbles in the extruded rice. In particular, compared with raw rice, the WAI and WSI of ERPSP was higher, and the thermal properties also changed noticeably. The results of XRD and FT-IR spectroscopy showed that the semicrystalline structure of extruded rice changed from A-type to A + V-type mixture, and the relative crystallinity of extruded rice changed accordingly. In addition, a significantly lower equilibrium hydrolysis (C∞) and kinetic constant (k) were observed in ERPSP. The novel rice product made from broken rice by extrusion processing and addition of the purple sweet potato exhibited improved structural properties and reduced digestibility, which increased the potential value and application of broken rice in the food industry.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...