Acute bio-augmentation effect of perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) on activated sludge in biological denitrification processes and related stress mechanisms†
Abstract
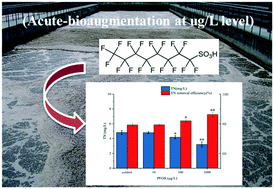
Perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) has been widely detected in wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs). Here, we investigated the nitrogen removal efficiency of activated sludge and related stress mechanisms in a sequencing batch reactor (SBR) after 8 h exposure to PFOS at 10, 100, and 1000 μg L−1. At 10 μg L−1, no significant effect (p > 0.05) was observed on total nitrogen (TN) removal. However, the TN removal efficiency significantly increased from 79.24% (control) to 81.99% and 86.21% at high concentrations (100 and 1000 μg L−1), respectively. In addition, the activities of nitrogen removal enzymes such as ammonia monooxygenase, nitrite oxidoreductase, nitrate reductase, and nitrite reductase were promoted by PFOS, which had variation trends similar to the TN removal rates. High throughput sequencing revealed that acute-term exposure to PFOS had little influence on the microbial richness (Chao) and diversity (Shannon) of activated sludge, but the relative abundance of most nitrogen-removing bacteria increased (Paracoccus, Thauera, and Comamonas increased from 0.43%, 1.78%, and 1.52% in the control to 0.60%, 2.13%, and 1.74% in SBR3, respectively), which could explain the increased nitrogen removal efficiency. This might be due to the protection of relevant bacteria by extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs), because the EPS evidently increased at 100 and 1000 μg L−1. However, an extremely significant (p < 0.01) increase of reactive oxygen species production and lactate dehydrogenase release at 100 and 1000 μg L−1 PFOS showed that PFOS caused oxidative damage and destroyed the integrity of microbial cell membranes. This indicated that PFOS has an acute bio-augmentation effect on the nitrogen removal process in WWTPs, but causes cytotoxicity after acute exposure.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...