Synthesis and biological evaluation of mixed-ligand cyclometalated iridium(iii)–quinoline complexes†
Abstract
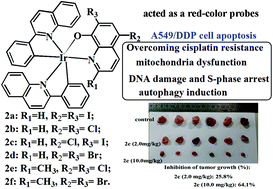
With the aim of gaining new insight into the underlying apoptosis mechanisms and in vivo efficacy of cyclometalated Ir(III) complexes as metalodrugs, six new cyclometalated Ir(III)–quinoline complexes, [Ir(1a)(2pq)2] (2a), [Ir(1b)(2pq)2] (2b), [Ir(1c)(2pq)2] (2c), [Ir(1d)(2pq)2] (2d), [Ir(1e)(2pq)2] (2e), and [Ir(1f)(2pq)2] (2f) (2pq = 2-phenylisoquinoline), have been synthesized using 5,7-dihalo-8-hydroxylquinoline ligands (1a–1f) and [Ir(2pq)2Cl]2 precursors and characterized. Complexes 2a–2f have shown potent anticancer activity against cisplatin-resistant SK-OV-3/DDP and A549/DDP cells (IC50 = 0.11–1.83 μM), following the order 2e > 2f > 2b > 2c > 2d > 2a. Confocal microscopy images suggest that 2e and 2b could act as red-color probes for specific cell imaging and efficiently initiate apoptosis and autophagy in the mitochondria, cell cytosol, and nucleus. Overexpression of beclin1, caspase-9, cytochrome c, LC3II, and apaf-1; inhibition of p62, cyclin D1, cyclin A2, and CDK2; and a substantial rapid accumulation suggest a paraptotic mode of cell death induced by autophagy, DNA damage, and mitochondrial stress. In addition, the inhibitory rate of 2e on A549/DDP tumor growth was 64.1% at a concentration of 10.0 mg kg−1, which is clearly higher than that of cisplatin. According to the biological assay, the cyclometalated Ir(III)–quinoline complex 2e exhibited a higher anticancer effect than 2b, which may be associated with the electronic effect of the methyl group of the 1e ligand of 2e playing a key role in the mechanism.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...