Comparing electrocatalytic and thermocatalytic conversion of nitrate on platinum–ruthenium alloys†
Abstract
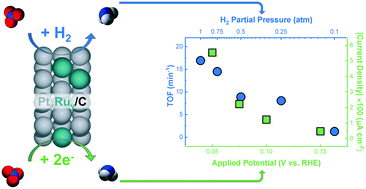
Nitrate is a significant water pollutant resulting from anthropogenic nitrogen fixation and other industrial processes. Heterogeneous thermocatalytic and electrocatalytic processes to convert nitrate to nitrogen or ammonia are proposed to follow similar reaction mechanisms. However, there are no studies comparing these two processes on the same catalyst surface under similar reaction conditions. Here, we study both reactions on a series of PtxRuy/C alloys to identify similarities and differences. For both reactions, we find that catalyst activity is correlated to both hydrogen and nitrate adsorption energies, signifying the importance of hydrogen and nitrate coverage in both systems. We show that PtRu catalysts, recently reported to enhance electrocatalytic nitrate reduction, are also more active for thermocatalytic nitrate reduction than Pt. However, the effect of pH on reaction rates is considerably different between the two reactions, indicating that electrochemical-specific steps differentiate the two processes. We analyze the cost of converting nitrate to ammonia through both thermocatalytic and electrocatalytic reduction under different conditions on the same catalyst to compare which process is more cost-effective and capable of approaching the rates of commercial Haber–Bosch ammonia production.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...