Bioinspired iron-loaded polydopamine nanospheres as green flame retardants for epoxy resin via free radical scavenging and catalytic charring†
Abstract
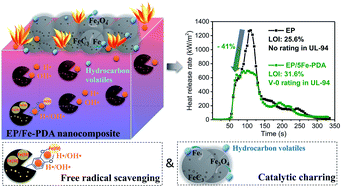
The versatile coating capability of polydopamine (PDA) has received much research interest in numerous fields, including flame retardant functionalization of fillers for polymers. However, the understanding of flame retardant actions of PDA materials in combustion still remains incomplete, limiting its practical applications and future designs as polymer reinforcing fillers. In this study, iron-loaded polydopamine (Fe-PDA) nanospheres were introduced into epoxy resin (EP) as green flame retardant additives. The resultant EP nanocomposites exhibited remarkably reduced flammability, reflected by the high LOI value of 31.6%, V-0 rating in the UL-94 test, as well as a 41% reduction in the peak heat release rate at 5 wt% Fe-PDA loading. More importantly, for the first time, it is clearly revealed that the flame inhibition action in the gas phase was owing to the free radical scavenging ability of Fe-PDA. In addition to the gas phase action, Fe-PDA also promoted the charring process in the condensed phase, leading to the formation of integrated char layers that effectively delayed the mass and heat transfer of combustion. Based on these actions (free radical scavenging and catalytic charring), Fe-PDA acted as the nontoxic and highly efficient flame retardant in EP.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...