MOF thin films with bi-aromatic linkers grown by molecular layer deposition
Abstract
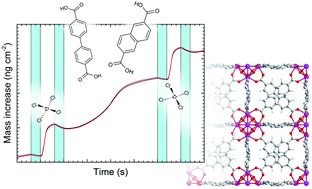
Thin films of metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) are promising for a wide range of applications including membranes for separations and sensor materials in microelectronics. Growth of such thin films using atomic/molecular layer deposition (ALD/MLD) has recently been demonstrated; however, the range of examples is still narrow. Here, we expand the repertory of gas-phase MOF thin film synthesis by ALD/MLD to include 2,6-naphthalenedicarboxylate (2,6-NDC) and biphenyl-4,4′-dicarboxylate (BP-4,4′-DC) as organic linkers. The films, which were deposited using ZrCl4 and either H2–2,6-NDC or H2–BP-4,4′-DC, were amorphous and formed crystalline MOF-structures when treated with acetic acid vapour at 160 °C. The film growth was investigated using in situ quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) measurements, and was in addition characterized using spectroscopic ellipsometry (SE), photoluminescence (PL), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), grazing incidence X-ray diffraction (GIXRD) and X-ray reflectivity (XRR). We further performed introductory investigations into a selection of possible future applications of these films, due to their porosity, luminescent and antibacterial properties. Expanding the repertory of MOF synthesis by ALD/MLD to include longer linkers such as 2,6-NDC and BP-4,4′-DC enables synthesis of thin films with a larger range of pore sizes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...