Effect of polymer–nanoparticle interaction on strain localization in polymer nanopillars†
Abstract
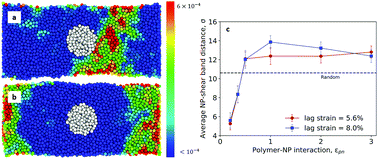
Polymer nanocomposites (PNCs), a class of composites consisting of typically inorganic nanoparticles (NPs) embedded in a polymer matrix, have become an emerging class of materials due to their significant potential to combine the functionality of NPs with the toughness of polymers. However, many applications are limited by their mechanical properties, and a fundamental understanding of NPs’ effect on the nonlinear mechanical properties is lacking. In this study, we used molecular dynamics simulations to investigate the influence of NPs on the tendency of a polymer nanopillar to form a shear band. Even though we restrict ourselves to sufficiently low NP loadings that the elastic and yield behaviors are unaffected compared to the pure polymer, the polymer–NP interactions have a surprisingly strong effect on the location of a shear band in the sample. Different polymer–NP interactions have been used to explore their effect on the local structure of materials which is described using a recently developed machine-learned quantity, softness. Our calculations reveal a strong correlation between the strain localization pattern and the local structural signatures. Lastly, we show that weak interactions between NP and polymer matrix can form a soft region near the NP, and this leads to an attraction of the shear band to the NP surface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...