Correlations between the structure and the vibrational spectrum of the phosphate group. Implications for the analysis of an important functional group in phosphoproteins†
Abstract
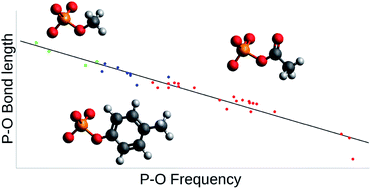
Density functional theory calculations were used to establish correlations between the structure and the vibrational spectrum of the phosphate group in model compounds for phosphorylated amino acids. The model compounds were acetyl phosphate, methyl phosphate, and p-tolyl phosphate, which represented the phosphorylated amino acids aspartyl phosphate, serine or threonine phosphate, and tyrosine phosphate, respectively. The compounds were placed in different environments consisting of one or several HF or H2O molecules, which modeled interactions of phosphorylated amino acids in the protein environment. The calculations were performed with the B3LYP functional and the 6-311++G(3df, 3pd) basis set. In general, the wavenumbers (or frequencies) of the stretching vibrations of the terminal P–O bonds correlated better with bond lengths of the phosphate group than with its bond angles. The best correlations were obtained with the shortest and the mean terminal P–O bond lengths with standard deviations from the trend line of only 0.2 pm. Other useful correlations were observed with the bond length difference between the shortest and longest terminal P–O bond and with the bond length of the bridging P–O bond.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...