Corrosion inhibition on mild steel in 1 M HCl solution by Cryptocarya nigra extracts and three of its constituents (alkaloids)
Abstract
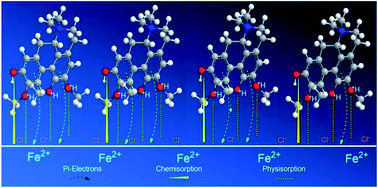
Corrosion inhibition effect of the crude extracts (hexane, dichloromethane, methanol) from the bark of Cryptocarya nigra and three alkaloids named N-methylisococlaurine 1, N-methyllaurotetanine 2 and atherosperminine 3 isolated from the Cryptocarya nigra dichloromethane extract (CNDE) were investigated for mild steel corrosion in 1 M HCl solution. An electrochemical impedance study showed that CNDE and 2 reduced the corrosion significantly through a charge transfer mechanism with inhibition efficiency of 91.05% and 88.05%, respectively. Potentiodynamic polarization data indicated that CNDE acted through anodic type inhibition while 2 was a mixed type inhibitor with predominant anodic effectiveness. ΔGads values calculated from the Langmuir adsorption isotherm plots for CNDE (−28.2 kJ mol−1) and 2 (−13.2 kJ mol−1) suggested that they adsorbed on the mild steel surface via a physisorption mechanism. Scanning electron microscopy micrographs and elemental composition studies confirmed the formation of a protective film over the metal surface. Wastewater quality parameters of all the inhibitors demonstrated good biodegradability as their values were within the permissible limits to discharge for irrigation and horticultural uses.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...