Erythrocyte membrane concealed paramagnetic polymeric nanoparticle for contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging†
Abstract
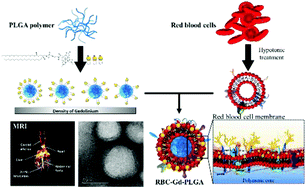
Recent progress in bioimaging nanotechnology has a great impact on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases by enabling early intervention. Among different types of bioimaging modalities, contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging using paramagnetic gadolinium-based molecular contrast agents (GBCAs) are most commonly used in clinic. However, molecular GBCAs distribute rapidly between plasma and interstitial spaces with short half-lives limiting its clinical impacts. To improve the properties of GBCAs, herein an effort has been put forth by incorporating GBCA into nanoscale system mimicking the property of red blood cell (RBC) that could facilitate contrast enhancement and prolong intraluminal retention in the body. The proposed nanoconstruct is made up of polymeric-core labeled with lipid conjugated GBCA followed by the imprint of the RBC membrane concealment layer to enhance stability and biocompatibility. Meanwhile, the confinement strategy of GBCA was implemented to accelerate magnetic properties of nanoconstruct providing longitudinal-relaxivity (r1) to 12.78 ± 0.29 (mM s)−1. Such improvement in r1 was further confirmed by enhanced contrast in the vascular angiography of the murine model. Given higher colloidal stability and tunable magnetic properties, nanoconstruct proposed herein is a promising platform technology for the applications where enhanced plasma residence time and magnetic properties are necessary for diagnosis and therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...