A glutathione-depleted prodrug platform of MnO2-coated hollow polydopamine nanospheres for effective cancer diagnosis and therapy†
Abstract
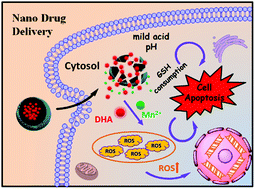
Currently, cancer is regarded as one of the most life-threatening diseases worldwide. To date, much attention has been paid to treating this serious disease. Among various cancer therapies, chemotherapy has been used in the clinic for more than sixty years and is regarded as an ideal choice because of its high efficiency. Herein, a biocompatible and efficient nanoplatform for tumor treatment was fabricated based on manganese oxide-coated hollow polydopamine (HPDA@MnO2). Dihydroartemisinin (DHA), a derivative of the Chinese traditional anti-malarial medicine artemisinin, was selected to be loaded into the cavity of HPDA@MnO2 to form the final nanodrug DHA@HPDA@MnO2. As a unique nanoplatform, DHA@HPDA@MnO2 showed biodegradable and controllable release of DHA and Mn ions upon reaching the tumor sites. It is worth mentioning that the reduced Mn2+ interacts with DHA to generate cytotoxic reactive oxygen species (ROS) which effectively damage proteins and nucleic acids, thereby inducing the death of tumor cells. More importantly, the Mn ions reduced from MnO2 showed selective in vivo magnetic resonance imaging capability in response to the tumor microenvironment. In vitro and in vivo therapy experiments showed that the tumor inhibition of DHA@HPDA@MnO2 was more efficient than that of free DHA, accompanied by negligible side effects; thus, the proposed nanomedicine platform is promising for application in tumor chemotherapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...