Novel 2-naphthyl substituted zinc naphthalocyanine: synthesis, optical, electrochemical and spectroelectrochemical properties†
Abstract
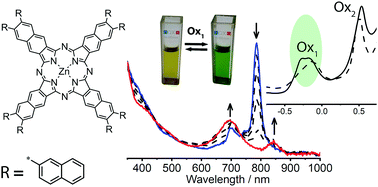
Novel near IR absorbing zinc 2,3-naphthalocyanine with bulky 2-naphthyl groups was obtained from corresponding 2,3-dicyanonaphthalene and characterized by mass spectrometry, UV-Vis, infrared and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR). Two-dimensional NMR was employed for full proton and carbon signal assignment in initial 2-naphthyl-substituted 2,3-dicyanonaphthalene. The main absorption maximum of 2-naphthyl-substituted naphthalocyanine complex at 790 nm shows a shift of 6 nm to the near IR region compared to phenyl-substituted analogues. The UV-Vis spectrum of the complex in o-DCB shows strong aggregation, which can be suppressed by N-containing agents or ternary ammonium salt due to steric hindrance or electrostatic repulsion. Pyridine demonstrates the most pronounced effect that reaches maximum value at 2 vol% pyridine. The monomeric form of the naphthalocyanine complex has a narrow Q band and well-resolved satellites. Since pyridine may play a role of both coordinating and reducing agent, fluorescence and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy were used to clarify the mechanism of its influence on the naphthalocyanine complex. Fluorescence properties (fluorescence and excitation spectra, fluorescence quantum yield) as well as electrochemical and spectroelectrochemical behavior were studied in o-DCB. The addition of pyridine results in a slight shift towards a higher value for the first oxidation and first reduction potentials. Moreover, the first oxidation process shows a split that increases after the addition of pyridine. Nevertheless, a single reversible one-electron transition was confirmed by spectroelectrochemical titration in the region of the first oxidation. The first oxidation process of the naphthalocyanine complex was accompanied by reversible color change from olive to bright green, which is not typical for naphthalocyanine complexes with other functional groups (e.g. unsubstituted, alkyl).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...