Robustness in glycosylation systems: effect of modified monosaccharides, acceptor decoys and azido sugars on cellular nucleotide-sugar levels and pattern of N-linked glycosylation†
Abstract
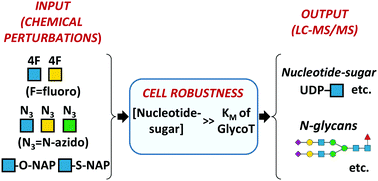
Small molecule monosaccharide analogs (e.g. 4F-GlcNAc, 4F-GalNAc) and acceptor decoys (e.g. ONAP, SNAP) are commonly used as metabolic glycoengineering tools to perturb molecular and cellular recognition processes. Azido-derivatized sugars (e.g. ManNAz, GlcNAz, GalNAz) are also used as bioorthogonal probes to assay the glycosylation status of cells and tissue. With the goal of obtaining a systems-level understanding of how these compounds work, we cultured cells with these molecules and systematically evaluated their impact on: (i) cellular nucleotide-sugar levels, and (ii) N-linked glycosylation. To this end, we developed a streamlined, simple workflow to quantify nucleotide-sugar levels using amide-based hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) separation followed by negative-mode electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS/MS) using an Orbitrap detector. N-Glycans released from cells were also procainamide functionalized and quantified using positive-mode ESI-MS/MS. Results show that all tested compounds changed the baseline nucleotide-sugar levels, with the effect being most pronounced for the fluoro-HexNAc compounds. These molecules depressed UDP-HexNAc levels in cells by up to 80%, while concomitantly elevating UDP-4F-GalNAc and UDP-4F-GlcNAc. While the measured changes in nucleotide-sugar concentration were substantial in many cases, their impact on N-linked glycosylation was relatively small. This may be due to the high nucleotide-sugar concentrations in the Golgi, which far exceed the KM values of the glycosylating enzymes. Thus, the glycosylation system output exhibits ‘robustness’ even in the face of significant changes in cellular nucleotide-sugar concentrations.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Glycomics & Glycoproteomics: From Analytics to Function


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...