Within-species variation in OMV cargo proteins: the Myxococcus xanthus OMV pan-proteome†
Abstract
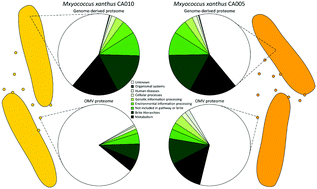
Extracellular membrane vesicles are produced by all domains of life (bacteria, archaea and eukaryotes). Bacterial extracellular vesicles (outer membrane vesicles or OMVs) are produced by outer membrane blebbing, and contain proteins, nucleic acids, virulence factors, lipids and metabolites. OMV functions depend on their internal composition, therefore understanding the proteome of OMVs, and how it varies between organisms, is imperative. Here, we report a comparative proteomic profiling of OMVs from strains of Myxococcus xanthus, a predatory species of Gram-negative myxobacteria whose secretions include secondary metabolites and hydrolytic enzymes, thought to be involved in prey lysis. Ten strains were chosen for study, of which seven had genome sequences available. The remaining three strains were genome sequenced allowing definition of the core and accessory genes and genome-derived proteins found within the pan-genome and pan-proteome respectively. OMVs were isolated from each strain and proteins identified using mass spectrometry. The M. xanthus OMV pan-proteome was found to contain tens of ‘core’ and hundreds of ‘accessory’ proteins. Properties of the OMV pan-proteome were compared with those of the pan-proteome deduced from the M. xanthus pan-genome. On average, 80% of ‘core’ OMV proteins are encoded by genes of the core genome, yet the OMV proteomes of individual strains contain subsets of core genome-derived proteins which only partially overlap. In addition, the distribution of characteristics of vesicle proteins does not correlate with the genome-derived proteome characteristic distribution. We hypothesize that M. xanthus cells package a personalized subset of proteins whose availability is only partially dictated by the presence/absence of encoding genes within the genome.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...