Specific ion effects control the thermoelastic behavior of nanolayered materials: the case of crystalline alkali-silica reaction products
Abstract
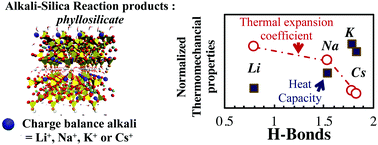
We perform molecular simulations to characterize the structure and the thermo-mechanical behavior of crystalline alkali-silica reaction (ASR) products, which are layered silicate analogous to shlykovite. As charge-balancing cations, we study Na and K (the most relevant alkali involved in ASR) as well as Li (relevant for ASR therapy) and Cs (relevant for nuclear applications). For the first time, the thermal and elastic properties of these crystalline products are computed using molecular simulations. The simulations reveal that the charge-balancing cations control thermo-elastic properties of shlykovite, following the example of other phyllosilicates. Change balance ion affects the number of H-bonds in the order Cs > K > Na > Li, and that observation can be associated with the variations in the computed thermo-mechanical properties. Using as input the elastic properties obtained from the molecular scale and assuming long-range disorder at the mesoscale (through a simplified representation of the gel scale), we provide mean-field homogenization estimates of the elastic constants at the gel scale that are consistent with indentation data. This result suggests a nanogranular texture of ASR gels.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...