Rapid evaluation of gold nanoparticle–lipid membrane interactions using a lipid/polydiacetylene vesicle sensor
Abstract
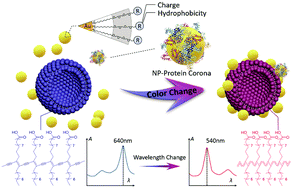
Surface modification of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) has significant and complicated effects on their interactions with cell membranes. In this study, we used a lipid/polyacetylene (PDA) vesicle sensor as the lipid membrane model to evaluate AuNP–lipid membrane interactions. Based on the colorimetric response (CR) of PDA vesicles before and after incubation with AuNPs, it was found that the interaction was highly dependent on the surface charge of AuNPs. As compared to the positively charged NPs, neutral and zwitterionic NPs adsorbed much less on the lipid membrane. Negatively charged NPs did not induce any noticeable color changes even at high concentrations. A class of cationic AuNPs with different degrees of surface hydrophobicity was further selected to investigate the role of hydrophobicity in interacting with lipid/PDA vesicles, and log(EC50) was employed as the evaluation index. According to the log(EC50)–NP concentration curve, the hydrophobicity of NPs enhanced the lipid membrane affinity, but electrostatic interactions weakened this effect. Finally, different concentrations of bovine serum albumin (BSA) were used to study the effect of the protein corona on NP–lipid membrane interactions. The formation of a NP–protein corona was found to mask the electrostatic interactions, leading to the decrease of the CR values of cationic NPs, and highly hydrophobic NPs were less affected by a low concentration of BSA due to the strong hydrophobic interactions. Although the effect of NP surface properties on their interactions with cells is far more complicated, our study provides a rapid and effective method for the evaluation of the interactions between surface modified AuNPs and lipid membranes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...