Achieving multiple hydrogen/deuterium exchange timepoints of carbohydrate hydroxyls using theta-electrospray emitters†
Abstract
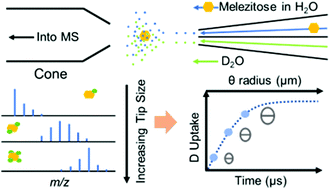
Hydrogen/deuterium exchange coupled to mass spectrometry (HDX-MS) is a well-established technique for structural analysis of proteins. In HDX experiments it is common to label for multiple, different lengths of time to characterize protein structures and dynamics. However, applications of HDX to carbohydrates have been limited due to the rapid exchange rates of hydroxyls, which have also prevented the development and application of methods that sample HDX at multiple timepoints. Theta capillaries pulled to electrospray tips have been used to achieve microsecond reaction times. Here, we report the utilization of theta-ESI emitters to achieve multiple timepoints for deuteration of carbohydrates. We increased the labeling time for HDX by increasing the initial ESI droplet sizes using theta-ESI emitters with increasing tip opening sizes. The reaction times achieved by varying the tip sizes ranged from sub-microsecond to ∼20 μs, with the average number of deuterium exchanges varying from 0.5 ± 0.2 D to 5 ± 3 D for sodium-adducted melezitose, which contains 11 labile hydrogens. Our findings are significant because this is the first report of carbohydrates analyzed by solution-phase HDX to achieve multiple H/D exchange timepoints.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...