Androgenic/antiandrogenic activities of PAEs determined by a novel AR-mediated reporter gene assay based on LLC-MK2 cells
Abstract
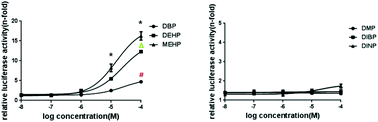
Recent reports have concentrated on some androgens/antiandrogens and confirmed that certain chemicals have demonstrated androgenic/antiandrogenic activities in vitro. However, it is still unknown whether more chemicals in the human environment possess endocrine toxicity. 58A novel AR-mediated reporter gene assay based on LLC-MK2 cells was established by transiently co-transfecting with pARE-sv40-Luc, hAR-pcDNA3.1 and pRL-tk. pARE-sv40-Luc was constructed using a pGL3-promoter plasmid with three repeated androgen responsive elements. hAR-pcDNA3.1 was constructed using pcDNA3.1 with a hAR sequence. After transfection for 12 h, the culture medium was exposed to various concentrations of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and other test chemicals (phthalic acid esters and dexamethasone) in order to measure the androgenic/antiandrogenic activity. The assay possessed a concentration-dependent response to DHT from 10−12 M to 10−6 M. Nilutamide concentrations of over 10−7 M completely blocked the luciferase expression induced by 10−9 M DHT. Other data showed that DBP, DEHP and MEHP possessed weak androgenic activity for certain concentration ranges, while DMP, DINP and DIBP did not show any androgenic activity. Moreover, five PAEs (DBP, DEHP, DINP, DIBP and MEHP) showed corresponding antiandrogenic activities for certain concentrations with an approximate tendency (MEHP > DBP > DEHP > DIBP > DINP). The assay is high-throughput, specific, and sensitive for the detection of androgenic/antiandrogenic chemicals. In addition, PAEs (especially transitional PAEs) exhibited corresponding androgenic/antiandrogenic activities for certain concentration ranges.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...