A water-resilient carbon nanotube based strain sensor for monitoring structural integrity†
Abstract
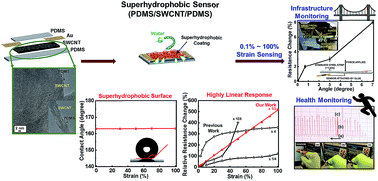
Monitoring structural integrity during and after extreme events such as an earthquake or a tsunami is a mundane yet important task that still awaits a workable solution. Additionally, the mechanical frame strength of transportation must be continuously monitored for sufficient safety. Currently available sensors are not sufficiently robust and are affected by humidity. A water-proof strain sensor would be applicable for infrastructure safety management in harsh environments and also as an advanced wearable sensor. Here, we develop a strain sensor based on single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) encapsulated in a non-fluorinated superhydrophobic coating, providing water resistance during elastic deformation, even at 100% strain. This newly developed sensor also offers highly linear piezoresistive behaviour owing to stretchable SWCNT networks. The superior water resiliency of the sensor, along with its appealing linearity and high stretchability, demonstrates the scalability of this approach for fabricating efficient strain sensors for applications in infrastructure and robotic safety management.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...