Mechanistic study on NO reduction by sludge reburning in a pilot scale cement precalciner with different CO2 concentrations
Abstract
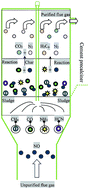
An experimental study on the effects of CO2 concentration on the release of reducing gases and the NO reduction efficiency by sludge reburning was carried out in a pilot scale cement precalciner. The results indicate that sludge reburning shows an ideal NO reduction activity. The best NO reduction efficiency of 54% is reached when the CO2 concentration is 25 vol%. Characteristic analysis of the sludge shows that the main types of reducing gases generated by sludge reburning are HCN, NH3, CO and CH4. Among them, CO2 concentration plays a crucial role in the release of HCN, CO and CH4. The mechanistic study indicates that NO reduction is dominated by homogeneous reduction during the sludge reburning process, in particular the reducing gases of CO and NH3 have significant influences on the NO reduction. Meanwhile, the effect of CO2 concentration on NO reduction is mainly due to the difference in CO release. The results of the present study not only provide insight into the mechanism of NO reduction by sludge reburning, but could also contribute to the development of NOX removal technology in the cement industry.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...