Electrodeposition of amorphous WO3 on SnO2–TiO2 inverse opal nano-framework for highly transparent, effective and stable electrochromic smart window†
Abstract
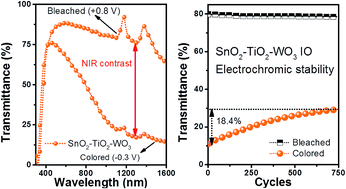
In recent years, there has been significant advancement in smart window technologies due to their effectiveness in reducing energy consumption of indoor lighting and air-conditioning in buildings. Electrochromic (EC) materials, in particular, have been widely studied as they provide a simple method for tuning or modulating visible light and infrared (IR) transmittance. In this work, a novel hybrid, multi-layered SnO2–TiO2–WO3 inverse opal (IO) nanostructure has been fabricated via dip-coating and electrodeposition process. This hybrid nanostructure allows an electrochromic smart window for effective near infrared (NIR) modulation, with high visible transparency and durable EC cycling stability. The visible transparency of as-fabricated hybrid multi-layered SnO2–TiO2–WO3 IO was measured to be in the range of 67.2–88.0% in the bleached state and 67.0–74.4% in the colored state, respectively. Furthermore, the hybrid nanostructure is also able to modulate up to 63.6% NIR radiation at the wavelength of 1200 nm and maintain approximately 82.6% of its NIR blockage capability after 750 reversible cycles. The hybrid multi-layered SnO2–TiO2–WO3 IO nanostructure in this study can potentially be an effective and stable EC material for advanced smart window technology.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...