A bromine-catalysis-synthesized poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/graphitic carbon nitride electrochemical sensor for heavy metal ion determination†
Abstract
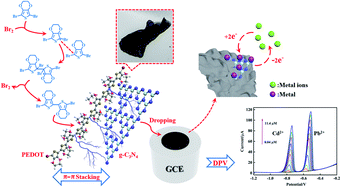
In this paper, poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/graphitic carbon nitride (PEDOT/g-C3N4) composites were prepared by the bromine catalysed polymerization (BCP) method with varying weight ratios of monomer to g-C3N4. For comparison, solid-state polymerization (SSP) and metal oxidative polymerization (MOP) methods were also used for the synthesis of PEDOT/g-C3N4 composites. Electrochemical determination of heavy metal ions (Cd2+ and Pb2+) was carried out by differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) on composite-modified glass carbon electrodes (GCEs), which were prepared by different methods. The obtained composites were analysed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), ultraviolet-visible absorption spectroscopy (UV-vis), X-ray diffraction (XRD), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The results showed that the bromine catalysed polymerization (BCP) method is an effective way to prepare the PEDOT/g-C3N4 composite, and the combination of PEDOT with g-C3N4 can improve the electrochemical activity of electrode materials. And, the composite from the BCP method modified electrode (PEDOT/10 wt% g-C3N4/GCE) exhibited the widest linear responses for Cd2+ and Pb2+, ranging from 0.06–12 μM and 0.04–11.6 μM with detection limits (S/N = 3) of 0.0014 μM and 0.00421 μM, respectively.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...