Transmembrane H+/Cl− cotransport activity of bis(amido)imidazole receptors†
Abstract
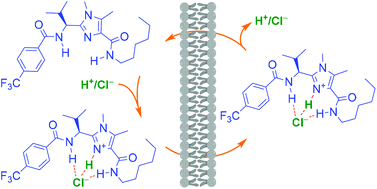
A series of sickle-shaped bis(amido) imidazoles are synthesized for their ion transport studies. Proton–anion binding by the neutral and protonated form of receptors assessed by 1H-NMR titration experiments confirmed better chloride binding by the protonated form of a receptor compared to its neutral form. The transport experiments across unimolecular vesicles (by HPTS and lucigenin assays) confirmed the H+/Cl− symport process under the applied pH gradient conditions. The transporter also allows anion antiport as evident from the studies under symmetrical pH conditions. The ionophoric activity by the mobile carrier mechanism is proved by the U-tube experiment.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Supramolecular chemistry in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...