Artificial muscle with reversible and controllable deformation based on stiffness-variable carbon nanotube spring-like nanocomposite yarn†
Abstract
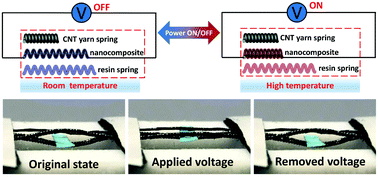
Carbon nanotube yarn actuators are in great demand for flexible devices or intelligent applications. Artificial muscles based on carbon nanotube yarn have achieved great progress over past decades. However, uncontrollable, small deformations and relatively slow deformation recovery are still great challenges for carbon nanotube yarn artificial muscles. Here we propose an artificial muscle based on a stiffness-variable carbon nanotube spring-like nanocomposite yarn. This nanocomposite yarn can be fabricated as artificial muscles by directly inflating epoxy resin on spring-like carbon nanotube yarn, and it shows a rapid response, and reversible and controllable deformation. The driving mechanism of the nanocomposite yarn artificial muscle is based on the change in the resin modulus controlled by Joule heat. This novel nanocomposite yarn artificial muscle can work at low voltages (≤0.8 V), and the whole reversible driving process is completed within 5 seconds (the deformation recovery process is about 2 seconds). The strain of the nanocomposite yarn artificial muscle is controlled by applied voltages, and the maximum strain can reach more than 12%. The novel nanocomposite yarn artificial muscle can produce output forces more than 20 times higher than human skeletal muscle. This CNT nanocomposite yarn artificial muscle with a spiral structure shows potential applications for actuators, sensors and micro robots.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...