Tuning the band gap of hybrid lead free defect perovskite nano crystals for solar cell applications†
Abstract
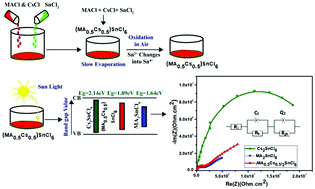
In recent reports, combinations of lead free organic inorganic halide perovskites have shown significant advances in solar cell devices. The aim of the present work is to prepare a defect ordered perovskite with nontoxicity, high stability and enhanced optoelectronic properties. We report the synthesis of high band gap cesium doped with methyl ammonium tin chloride ([(CH3NH3)0.5(Cs)0.5]2SnCl6, [(MA0.5Cs0.5)2SnCl6]) defect perovskite nanocrystals for multi junction solar cell applications. The substitution of inorganic cesium metal cations with organic methyl ammonium cation nanocrystals in the ratio of 50 : 50 at the A site was performed to modulate the band gap level and enhance the thermal stability. The crystallinity, vibrational state analysis, thermal stability and surface morphology of the synthesised compounds were investigated. UV-vis and photoluminescence measurements revealed that the band gap value is tunable and the band gap value obtained for (MA0.5Cs0.5)2SnCl6 is 1.89 eV. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) studies showed enhanced thermal stability for (MA0.5Cs0.5)2SnCl6 since the weight loss is meagre until it attains 900 °C. The electrical properties of (MA0.5Cs0.5)2SnCl6 were studied using Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) studies. EIS studies showed the recombination process was controlled for the (MA0.5Cs0.5)2SnCl6 perovskite material by proper electron transfer, which may lead to an increase in the efficiency of solar cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...